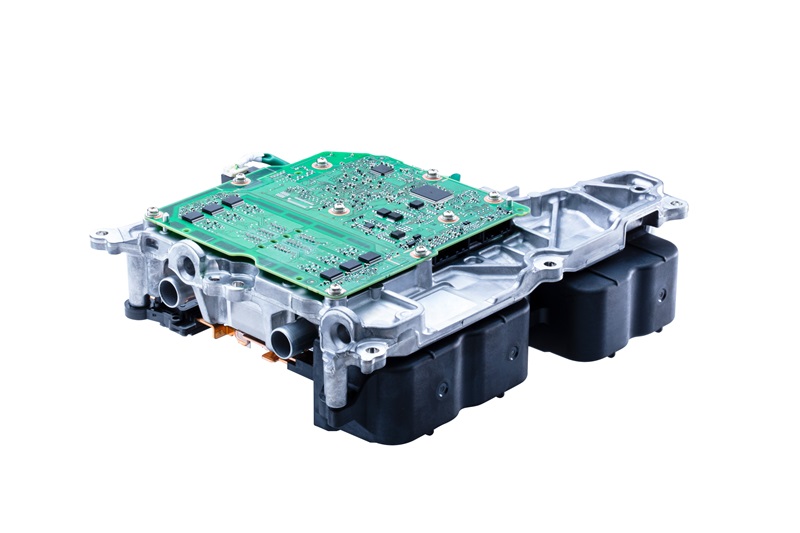
DENSO CORPORATION announced that it has developed its first-ever inverter with silicon carbide (SiC) semiconductors. This inverter, which is incorporated in the eAxle, an electric driving module developed by BluE Nexus Corporation, will be used in the new RZ, Lexus’ first dedicated battery electric vehicle (BEV) model.
SiC power semiconductors consist of silicon and carbon that significantly reduce power loss compared with silicon (Si) power semiconductors. The verification of cruising test in a certain condition, which test was performed by BEV consisted of SiC semiconductor inverters, demonstrated inverters with SiC power semiconductor reduce power loss less than half of ones with Si semiconductor. As a result, the energy efficiency of BEVs is improved and cruising range is extended.

SiC power semiconductors with DENSO’s unique trench-type metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) structure improve the output per chip due to reducing the power loss caused by heat generated. The unique structure achieved high voltage and low on-resistance operation.
Based on the high-quality technology jointly developed by DENSO and Toyota Central R&D Labs., Inc., we utilize SiC epitaxial wafers that incorporate the results of work commissioned by New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO). As a result, we have halved the number of crystal defects that prevent the device from operating normally due to the disorder of the atomic arrangement of the crystal.
By reducing crystal defects, the quality of SiC power semiconductor devices used in vehicles and their stable production are ensured.
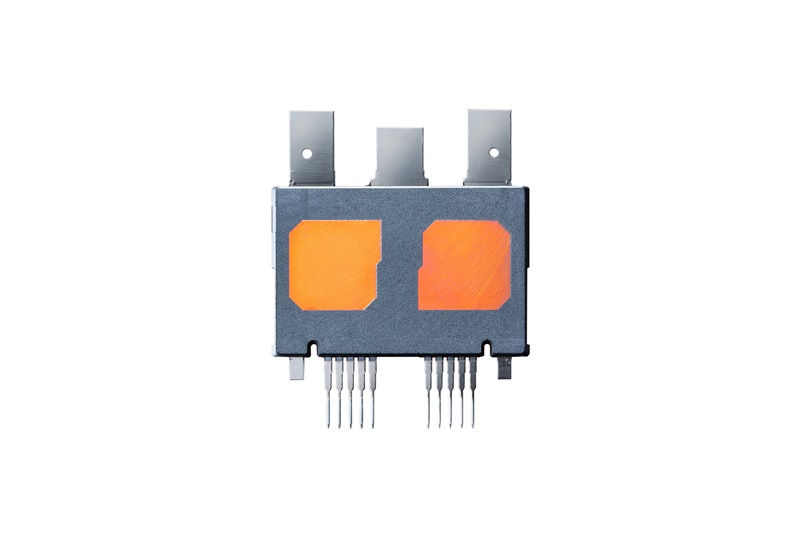
DENSO calls its SiC technology “REVOSIC®,” and uses it to comprehensively develop technologies for products ranging from wafers to semiconductor devices and modules such as power cards.