Renesas Electronics Corporation today announced that it has developed four technologies for system-on-chip (SoC) devices for in-vehicle communication gateways. These SoCs are expected to play a crucial role in defining the next-generation electrical/electronic (E/E) architecture in automotive systems.
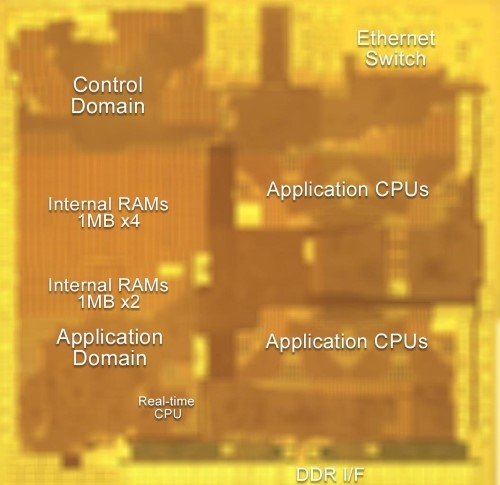
SoCs for automotive gateways must provide both high performance to implement new applications such as cloud services, and low power consumption when they are not in use. They also need to deliver fast CAN response to support instant start-up. Additionally, these SoCs need to provide power-efficient communication technology that enables network functions as a gateway using limited power and security technology to enable safe communication outside the vehicle.
To meet these requirements, Renesas has developed
1. Architecture that optimizes processing performance and power consumption depending on vehicle conditions
Communication gateway SoCs need to deliver processing performance exceeding 30,000 Dhrystone million instructions per second (DMIPS) when running, while also keeping standby power consumption to 2 mW or less in order to maintain battery life. Typically, high-performance SoCs also have high power consumption in standby mode, while low-power SoCs with small standby power consumption have performance issues. To resolve this tradeoff, Renesas combined in a single chip a high-performance application system and a control system optimized for ultralow standby power consumption. The new architecture controls the power supplies of these two subsystems and changes the timing of circuit operation to achieve an optimal balance between performance and power efficiency. This results in higher performance during operation and lower power consumption during standby.
2. Fast start-up technology with external flash memory achieving the same fast speed as embedded flash memory
Since communication gateway SoCs manage processing of critical functions related to vehicle control, they must be able to respond to CAN within 50 milliseconds (msec.) of start-up. However, if the SoC uses a process that does not support embedded flash memory, the start-up program must be encrypted and stored in external flash memory. This means that it takes additional time to load program data and decrypt it. To solve this issue, Renesas developed technology that splits the program into sections and initially loads and decrypts only an essential portion for start-up, while continuing to load the rest of the program in parallel. This enables a fast response to CAN (50ms or less), even when using external flash memory.
3. Highly efficient network accelerator with 10 Gbps/W communication efficiency
To allow air cooling and heat dissipation for electronic control units (ECUs), communication gateway SoCs must keep power consumption to 7 watts or less. Since computing processing performance of 30,000 DMIPS or higher requires approximately 6 watts of power, only around 1 watt can be used for network processing. This presents a challenge as the total communication of 10 Gbps must be achieved using 1 watt of power, with a processing efficiency of only around 3 Gbps/W when processed by the CPU. To work around this issue, Renesas offloaded processing from the CPU to a custom network accelerator, achieving higher efficiency at 9.4 Gbps/W. Additionally, Renesas boosted efficiency to 11.5 Gbps/W by switching the routing method from a conventional TCAM approach to a hash table in SRAM.
4. Security technology to prevent interference with communication requiring high reliability
A communication gateway SoC performs a mixed set of tasks such as data processing related to vehicle control that requires a high level of reliability, and large amounts of random data communication with cloud services and others. Since vehicle control is essential to ensuring safety, protecting and separating mission-critical data is important. However, despite the differences in data types, all data is transmitted through the same in-vehicle network, leading to physical intersections and raising security issues. To address this challenge, Renesas developed security technology that analyzes incoming packets to the SoC. It determines whether or not they contain essential data, and assigns them to different pathways and control functions within the network accelerator. This prevents interference with data that requires high reliability and safeguards in-vehicle data communication from a variety of security threats.
These four technologies have been incorporated into Renesas’ R-Car S4 vehicle communication gateway SoC. With the latest R-Car S4, developers can accelerate advances in E/E architectures, implement secure connection with cloud services, and ensure safe and reliable vehicle control at the same time.














