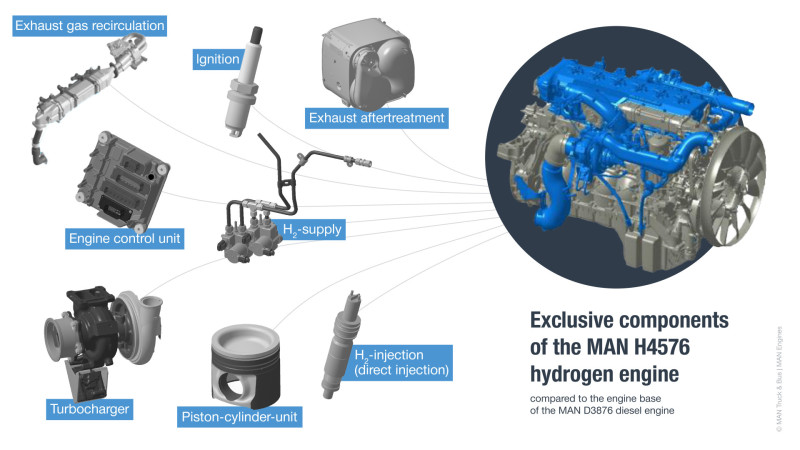
In connection with sustainable drive solutions for agricultural machinery and off-road applications, MAN Engines presents the MAN H4576.
The basis for the MAN H4576 is the established MAN D3876 diesel engine. This shares about 80% of its basic components such as the crankcase, crankshaft, connecting rods as well as the cooling and oil circuits including pumps, oil pan and filter with the new hydrogen engine. The almost identical dimensions of the two combustion engines make it easier for machine manufacturers to integrate them into existing vehicle concepts.
An important change, however, is the increase in bore from 138 mm to 145 mm, while the stroke remains unchanged at 176 mm. This modification to a larger displacement of 16.8 liters compared to the 15.3 liters of the MAN D3876 diesel engine is necessary in view of the lower power density of hydrogen engines in order to achieve the target power. Significant modifications were made to the components for hydrogen supply and combustion, the engine control system and the exhaust gas control system:
The hydrogen supply of the MAN H4576 comprises the system of new low-pressure lines and a rail, which supply the injector with the required hydrogen (chemically: H2). Precise pressure control is used to dose the hydrogen demand to ensure efficient combustion and optimally supply the engine with the fuel. The hydrogen injector is used for low-pressure direct injection with an injection pressure of up to 40 bar. It is mounted directly in the combustion chamber for higher performance and better engine response. The specially tuned ignition system takes these properties into account and enables reliable and controlled spark ignition of the hydrogen mixture. Among other things, the specially designed engine control unit controls the supply of hydrogen and air, regulates injection and ignition, and continuously adjusts the engine parameters to enable safe and efficient combustion. Compared to the diesel engine, the hydrogen combustion engine requires new pistons and liners, as the piston diameter has been increased to 145 mm. With 500 hp (368 kW), the resulting higher displacement achieves a similar performance to that of the MAN D2676 diesel engine with a displacement of 12.4 liters. The new turbocharger ensures optimum dynamics and helps to reduce fuel consumption.
The only relevant emissions that occur as potential by-products of H2 combustion and could end up in the exhaust gas to a significant extent are nitrogen oxides (NOx). In order to reduce this to almost zero, MAN Engines relies on an advanced combustion process and an established exhaust gas aftertreatment system. The combination of hydrogen combustion engine and exhaust gas aftertreatment meets the EU Stage V and Zero Emission Vehicle (ZEV) emission standards.