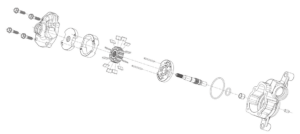
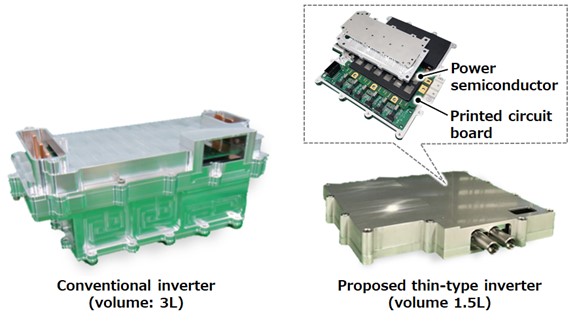
Hitachi and Hitachi Astemo have developed basic technology for a thin-type inverter that achieves both energy conservation and miniaturization as a power converter (hereinafter referred to as “inverter”) for electric vehicles (EVs). This technology simplifies power wiring by integrating power semiconductors that control power supply with printed circuit boards.
| Volume | Maximum output | Maximum current | Power density |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 L | 170 kVA | 350 A | 113 kVA/ℓ |
Hitachi and Hitachi Astemo have now developed a basic technology that avoids the problem of heat generation by integrating the power semiconductors on a printed wiring substrate that incorporates the inverter circuit components. This technology simplifies the power wiring inside the inverter and reduces inductance, resulting in a 30% reduction in the energy loss generated when the power semiconductors switch on and off, and thus reducing heat generation. The size of the inverter is also successfully reduced by 50% compared to conventional products.
Conventional inverters use many copper plate components called busbars*4 to supply large currents to power semiconductors, which must be connected by welding or other means. This required many parts and assembly processes, making it difficult to improve production efficiency. With the mounting technology, power semiconductors and circuit components are mounted on a compact, lightweight, thin printed wiring board, successfully eliminating the need for busbars. This has greatly simplified the production process, reducing the number of components and assembly steps. The technology reduces energy consumption in the production process and contributes to the reduction of CO2 emissions over the lifecycle of the inverter.